The global battery industry has witnessed a dramatic shift that fundamentally alters the automotive landscape. Chinese manufacturers now control 55% of the worldwide battery market, with industry leaders CATL and BYD commanding unprecedented dominance while Western competitors face systematic collapse. This transformation extends beyond mere market statistics to represent a complete restructuring of technological leadership, supply chain control, and economic power in the electric vehicle revolution.
The implications reach far beyond manufacturing numbers. Chinese battery technology has achieved superior performance metrics while maintaining cost advantages that Western manufacturers cannot match. As solid-state battery promises remain years away from commercial viability, Chinese companies continue expanding their technological and economic moats through vertical integration and manufacturing excellence.
For investors, consumers, and policymakers, understanding this market transformation has become essential. The battery industry’s evolution determines not only which electric vehicles will succeed but which countries will control the infrastructure of sustainable transportation. The data reveals a clear trajectory toward Chinese technological hegemony that challenges fundamental assumptions about Western innovation leadership.
The Magnitude of Chinese Dominance
CATL alone commands 38.1% of global electric vehicle battery installations, representing the largest single share ever achieved by a battery manufacturer. This dominance reflects not temporary market conditions but sustained technological and economic advantages that continue expanding. BYD’s remarkable growth to 17.3% market share, with 62% year-over-year increase, demonstrates the depth of Chinese competitive strength across multiple companies.
The combined Chinese market position represents approximately two-thirds of global production capacity, creating unprecedented concentration in battery manufacturing. This consolidation enables economies of scale that Western competitors cannot replicate, even with significant government subsidies and support programs.
Korean manufacturers, previously considered Chinese competitors, face declining relative positions despite aggressive capacity expansion efforts. LG Energy Solution, once a market leader, dropped to 10.7% share despite billions in investment and government backing. Samsung SDI and SK On maintain even smaller positions while struggling against relentless Chinese cost advantages.
European and American manufacturers occupy marginal positions in the global market, relying primarily on government protection and subsidies rather than competitive advantages. Tesla’s partnership diversification away from Panasonic toward Chinese suppliers illustrates how even premium Western brands recognize Chinese technological leadership.
The market data represents more than statistical shifts. Chinese dominance stems from systematic advantages in government support, supply chain integration, and manufacturing excellence that compound over time. Competition based purely on performance and cost consistently favors Chinese manufacturers across all major market segments.
Cost Structure Advantages That Cannot Be Matched
Chinese battery manufacturers achieve production costs of $40-60 per kilowatt-hour while Western alternatives remain significantly higher, creating fundamental competitive moats. This cost leadership enables Chinese companies to offer superior performance specifications while maintaining healthy profit margins, forcing Western competitors into unsustainable pricing positions.
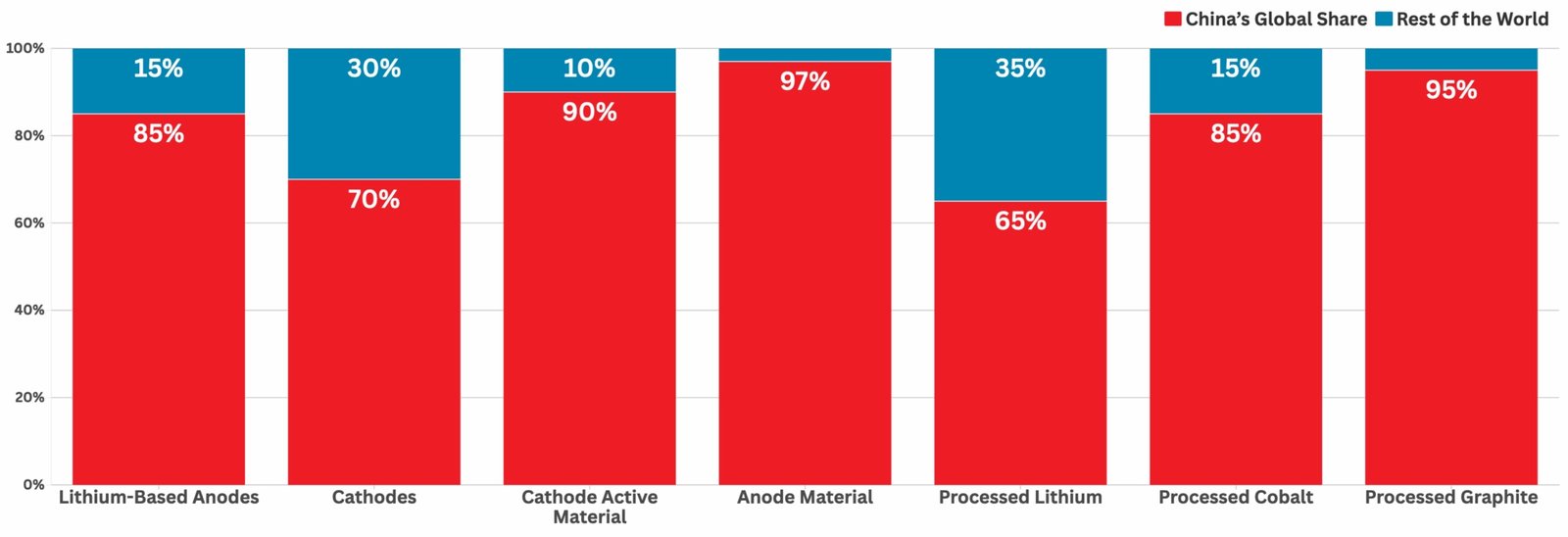
The cost advantages derive from multiple sources beyond labor arbitrage. Chinese companies control critical material processing including lithium refining, graphite production, and cathode manufacturing. This vertical integration eliminates supplier margins while ensuring consistent material quality and availability.
Manufacturing efficiency comparisons reveal Chinese factories achieving higher yields and faster production rates than Western alternatives. Automated production systems and process optimization contribute to cost advantages that scale with volume. Gigafactory operations in China demonstrate manufacturing sophistication that Western competitors struggle to replicate.
Quality control analysis shows Chinese manufacturers maintaining consistent performance across large production volumes. Statistical sampling indicates minimal variation in capacity, resistance, and safety characteristics, enabling reliable mass production quality that meets international automotive standards.
The raw material market dynamics have shifted dramatically, with lithium costs falling 80% from 2022 peaks to approximately $30,000 per ton. While this benefits all manufacturers, Chinese companies maintain structural advantages through supply chain control and processing capabilities that Western competitors depend upon despite political tensions.
Investment capital continues flowing toward Chinese battery development at record levels, with government and private funding supporting continued technological advancement and capacity expansion. The scale of investment commitment dwarfs Western efforts and ensures sustained competitive advantages over time.
Solid-State Battery Reality Check
While Western companies promote solid-state batteries as technological leapfrogs, manufacturing realities suggest delayed commercialization that may arrive too late to restore competitive balance. China’s solid-state battery competition with QuantumScape demonstrates how multiple companies pursue this technology simultaneously, though with varying timelines and commercial viability. QuantumScape’s QSE-5 batteries demonstrate impressive specifications with 844 watt-hours per liter energy density, but manufacturing costs remain hundreds of dollars per kilowatt-hour compared to Chinese conventional alternatives.
The Cobra separator production process represents genuine innovation, achieving 25 times faster heat treatment speeds than previous methods. However, scaling this breakthrough to gigawatt-hour production levels requires additional years of development and massive capital investment. Volkswagen PowerCo’s licensing partnership provides commercial pathways, but timeline predictions suggest limited deployment before 2027.
BMW’s real-world solid-state testing in Munich validates practical viability while revealing automotive-specific challenges including vibration tolerance, thermal management, and integration complexity. These engineering hurdles require solutions before commercial deployment, extending development timelines beyond initial projections.
Manufacturing equipment requirements differ substantially from conventional lithium-ion production, necessitating complete facility rebuilding rather than production line upgrades. The capital intensity of solid-state deployment creates additional barriers for Western manufacturers already struggling with conventional battery competitiveness.
Toyota’s development timeline suggests commercial solid-state deployment beginning 2027-2028 in limited applications, initially targeting hybrid vehicles before pure electric applications. Even optimistic projections indicate mass market adoption delayed until 2030 or beyond, providing Chinese manufacturers additional years to advance conventional technologies.
Technical challenges persist with dendrite formation, interface stability, and cycle life optimization requiring continued research investment. Multiple competing approaches including ceramic, sulfide, and polymer electrolytes fragment development resources while increasing overall uncertainty about commercial viability.
The fundamental question involves whether solid-state advantages justify development costs and timeline delays compared to rapidly advancing Chinese conventional batteries. Current Chinese technology delivers excellent performance, proven manufacturing scalability, and immediate availability at competitive costs.
Real-World Performance Analysis
Independent testing institutions confirm Chinese battery technologies meet or exceed manufacturer performance claims across critical metrics. German TÜV laboratories validated CATL Naxtra specifications through standardized automotive protocols, while Korean research facilities confirmed BYD Blade charging performance under controlled conditions.
Temperature performance testing reveals dramatic advantages for Chinese sodium-ion technology, with CATL Naxtra batteries maintaining 90% capacity at -40°C while conventional lithium-ion systems lose 30-50% capacity. Scandinavian testing facilities confirmed these results through extended Arctic exposure simulating Nordic winter conditions.
Cycle life analysis demonstrates Chinese technologies significantly outlasting Western alternatives in accelerated testing. CATL Naxtra exceeded 10,000 cycles while BYD Blade batteries showed capability for over 1.2 million kilometers of vehicle operation. Tesla’s 4680 improvements remain below Chinese benchmarks despite advancement over previous generations.
Charging consistency proves superior for Chinese batteries, with CATL and BYD maintaining rated speeds throughout charging sessions while Western alternatives experience thermal throttling during extended fast charging. Real-world infrastructure testing shows Chinese technologies performing better across diverse charging networks compared to manufacturer-optimized systems.
Safety testing confirms Chinese claims regarding improved thermal stability and reduced fire risks. Independent abuse testing validated manufacturer specifications with nail penetration and crush tests producing minimal thermal responses. International certification processes confirm Chinese batteries meet global automotive requirements for commercial deployment.
Manufacturing quality demonstrates Chinese companies achieving consistent performance across large production batches. European automotive testing institutes conducted comparative studies showing Chinese technologies consistently achieving superior results while maintaining cost advantages that enable broader market access.
The battery technology revolution parallels other breakthrough innovations like China’s nuclear batteries lasting 50 years and Swedish structural battery composites, demonstrating how technological leadership can shift rapidly when companies achieve breakthrough manufacturing capabilities combined with cost advantages.
Investment Implications and Market Predictions
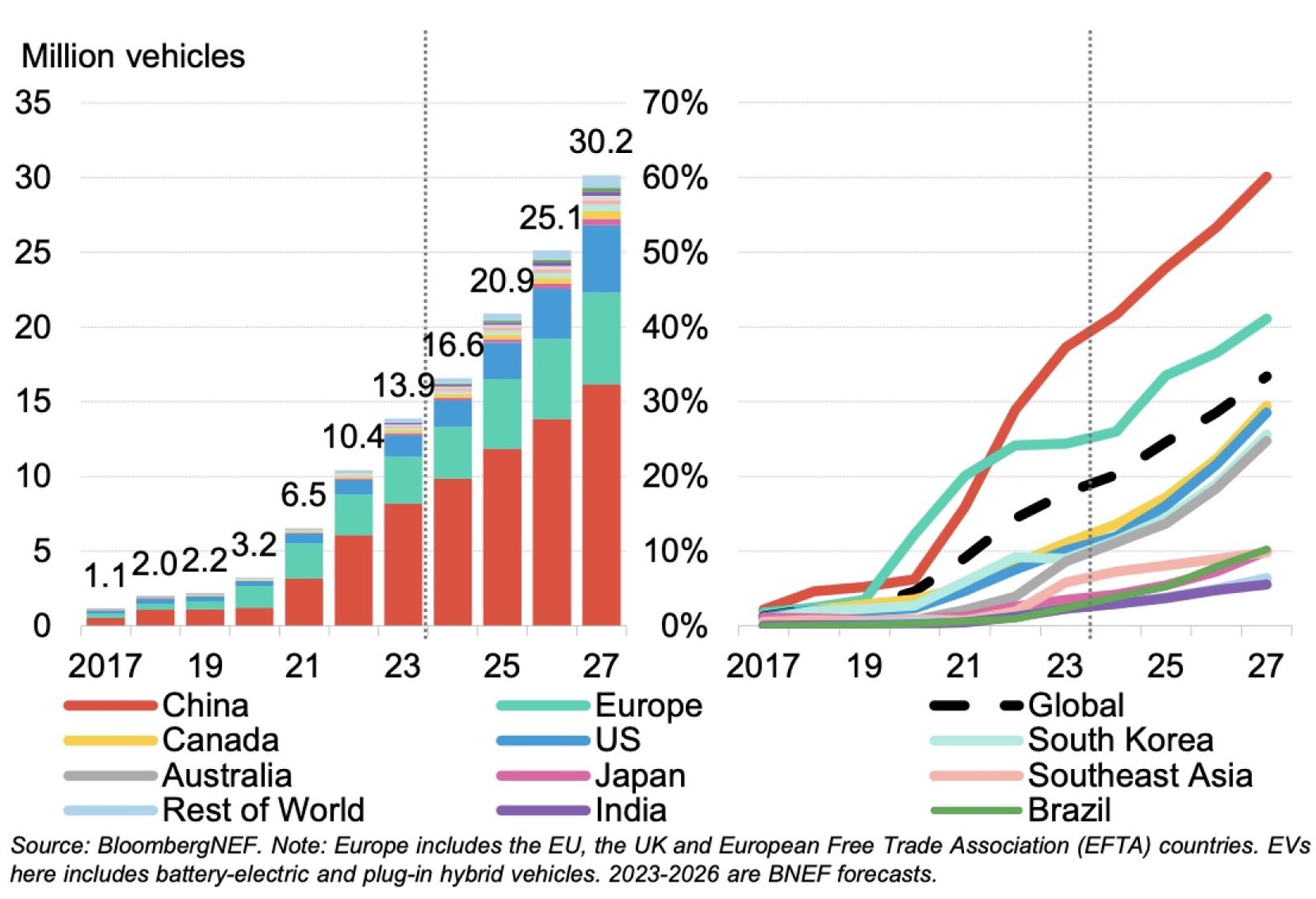
Financial markets increasingly recognize Chinese battery technology leadership through sustained stock performance and investment flows. CATL and BYD provide direct exposure to fastest-growing battery technologies with established commercial success and expanding market positions.
Chinese manufacturers report strong profit margins while Western competitors require government subsidies for basic viability. This fundamental difference in business model sustainability creates long-term investment implications that extend beyond cyclical market conditions.
Market timing suggests current periods offer optimal investment opportunities before Chinese dominance becomes universally recognized by mainstream financial analysts. Early positioning in leading Chinese battery companies provides maximum appreciation potential as competitive realities become apparent to broader markets.
Tesla’s 4680 program achievements help the company’s competitiveness but Chinese manufacturers maintain superior performance-to-cost ratios according to independent analysis. Tesla investors should consider battery technology limitations when evaluating long-term competitive positioning against advancing Chinese alternatives.
Solid-state battery investments remain speculative despite technical progress, with commercial viability requiring several additional years of development. QuantumScape and similar companies face execution risks while competing against rapidly advancing conventional technologies that already meet most consumer requirements.
Investment portfolio diversification should include exposure to Chinese battery technology leaders while maintaining positions in Western innovation companies for technological breakthrough potential. Geographic and technological diversification reduces concentration risk while capturing growth opportunities across multiple scenarios.
The convergence of battery technology with advanced manufacturing capabilities demonstrates how comprehensive battery technology developments in 2025 reshape multiple industrial sectors simultaneously. China’s million-mile battery competition between CATL and Tesla illustrates how durability advances complement cost leadership in creating market dominance.
Consumer Guidance for Electric Vehicle Purchases
For consumers evaluating electric vehicle purchases in 2025, this analysis provides clear guidance based on comprehensive performance data and market trends. Vehicles equipped with CATL batteries offer superior longevity and temperature performance, while BYD Blade technology provides fastest charging capabilities currently available.
Chinese battery technologies generally deliver better value propositions than Western alternatives when comparing total cost of ownership, performance specifications, and expected service life. Independent testing confirms these advantages reflect genuine technological superiority rather than subsidized pricing alone.
Tesla vehicles benefit from integrated design optimization and software advantages, but battery technology no longer provides competitive differentiation. Consider Tesla for charging network access and software capabilities rather than pure battery performance when evaluating purchase decisions.
Upcoming sodium-ion vehicles launching in 2026 deserve serious consideration for budget-conscious buyers seeking advanced performance capabilities. CATL Naxtra technology enables dramatically lower purchase prices while providing excellent cold weather operation and extended service life.
Solid-state battery vehicles remain several years away from mass market availability, with initial deployment limited to expensive premium models. Current solid-state promises exceed near-term delivery capabilities, requiring realistic expectations about commercialization timelines and initial pricing levels.
Charging infrastructure compatibility increasingly favors Chinese battery technologies as global deployment expands beyond proprietary networks. Fast charging advantages from BYD and CATL batteries provide practical benefits for daily usage patterns across diverse geographic regions.
Vehicle leasing strategies protect against rapid battery technology advancement while providing access to latest developments. Three-year lease terms avoid technology obsolescence risks during periods of accelerated innovation while enabling upgrading to newer technologies as they become available.
Supply Chain Control and Geopolitical Implications
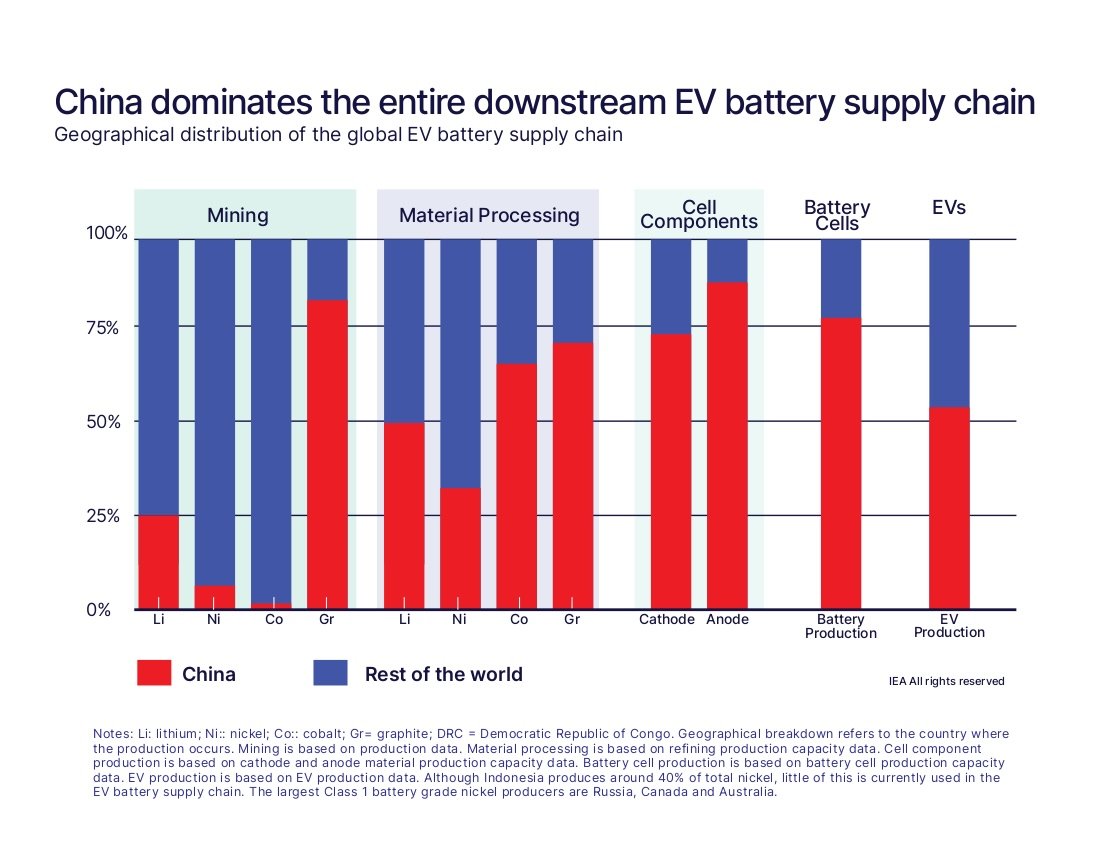
China’s dominance extends beyond manufacturing to include control of critical material processing and supply chain infrastructure. Chinese companies process the majority of lithium, refine graphite production, and manufacture cathode materials, creating dependencies for Western manufacturers despite ongoing political tensions.
Vertical integration advantages increase as competition intensifies and profit margins compress across the industry. Chinese companies control mining operations, material processing, and finished product manufacturing, capturing value across the entire supply chain while reducing external dependencies.
Government policies significantly influence market evolution through trade restrictions, subsidies, and local content requirements that favor domestic manufacturers. US tax credits require increasing percentages of materials from domestic or allied sources, while European regulations mandate carbon footprint disclosure and recycling content minimums.
Trade policy implications include potential export restrictions on critical materials and finished battery products. China’s graphite export controls demonstrate leverage over global battery supply chains, while Western countries pursue supply chain diversification strategies that struggle to match Chinese cost structures.
Manufacturing capacity expansion targets exceed 6 terawatt-hours by 2030, with Chinese factories accounting for the majority of planned additions. This capacity growth could temporarily create oversupply conditions while establishing permanent structural advantages for Chinese manufacturers.
Regional market preferences influence technology adoption patterns, with Chinese manufacturers dominating Asian markets while maintaining growing presence in European and North American segments. Political considerations may temporarily protect domestic manufacturers, but technological and economic advantages typically prevail over time.
According to Reuters analysis of competing battery technologies, Chinese battery manufacturers have achieved cost reductions of 85% since 2010 while Western competitors struggle to match these improvements despite significant government support programs. CarNewsChina reports that CATL and BYD collectively hold 66.6% market share in the first half of 2025, even higher than the 55% figure used earlier in this analysis.
Future Market Structure and Competitive Dynamics
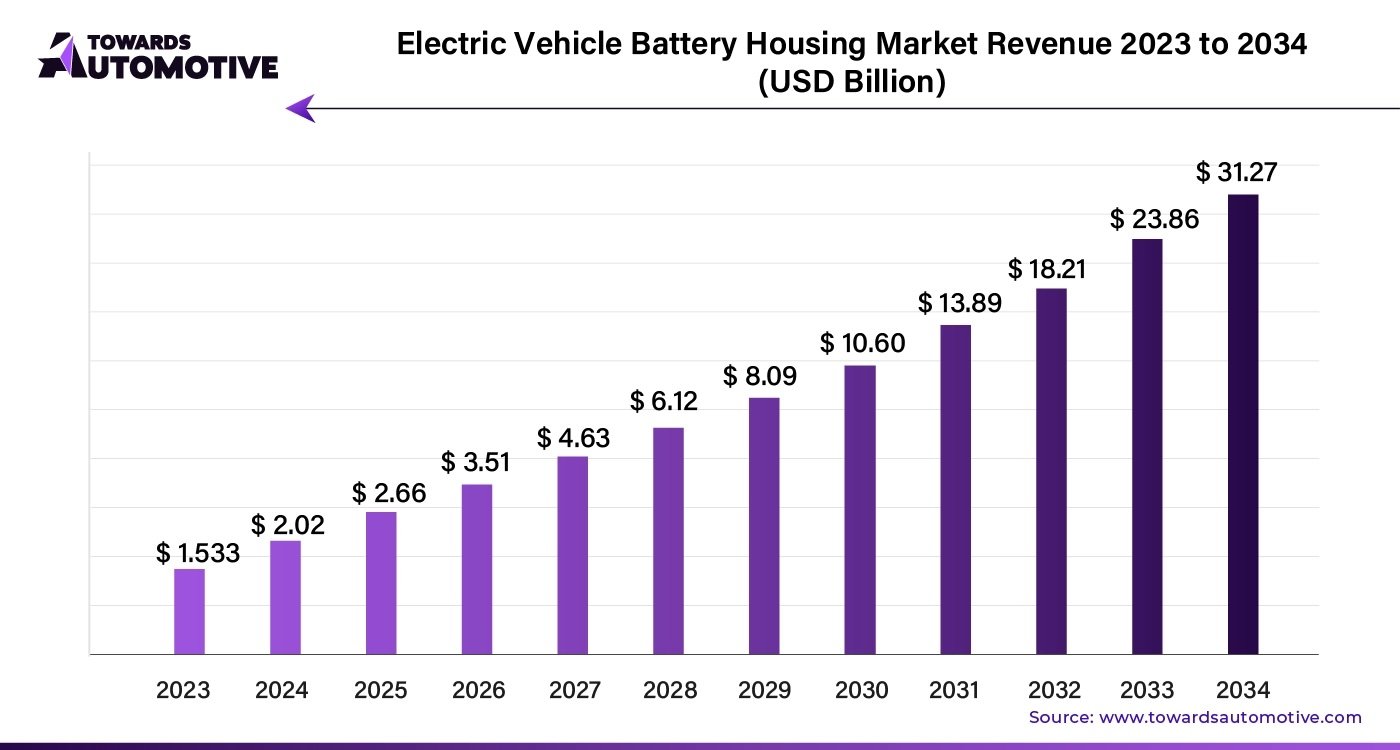
Future market evolution likely favors continued Chinese expansion unless Western manufacturers achieve breakthrough technological advantages or receive sustained political protection. Forbes analysis of solid-state batteries indicates that despite promising developments, significant commercial hurdles remain before this technology can challenge Chinese conventional battery leadership.
According to Battery Tech Online reporting on FDD analysis, China’s battery dominance threatens US economic security, with current trends suggesting Chinese companies will control majority market share across most geographic and application segments. The electric vehicle supply chain has become increasingly dependent on Chinese manufacturing and material processing capabilities.
Technology innovation accelerates across all major players with breakthrough announcements occurring monthly rather than annually, but Chinese companies consistently translate innovations into commercial products faster than Western competitors. This execution advantage compounds over time as market positions strengthen.
Market consolidation trends favor larger manufacturers with extensive research capabilities and manufacturing scale. Smaller battery companies face increasing difficulty competing against major players with superior resources, technical capabilities, and established customer relationships.
Competition intensity increases as market growth attracts new entrants while existing players expand capacity aggressively. Price competition benefits consumers while pressuring manufacturer margins, favoring companies with structural cost advantages and operational efficiency.
Financial performance data consistently shows Chinese manufacturers achieving sustainable profitability while Western competitors struggle with losses and dependence on government support. This fundamental business model difference determines long-term survival and growth potential across different companies.
The battery technology landscape reveals clear winners and losers with implications extending beyond automotive applications into energy storage, grid systems, and portable electronics. Chinese leadership in battery technology provides foundation advantages across multiple growing technology sectors.
Research from BloombergNEF indicates that Chinese manufacturers have achieved average battery pack prices 40% lower than international competitors, creating insurmountable cost advantages that compound through economies of scale.
Critical Assessment and Limitations
While Chinese battery technology leadership appears overwhelming based on current data, several factors could potentially alter competitive dynamics. Breakthrough innovations in solid-state technology, alternative battery chemistries, or manufacturing processes could provide Western companies with temporary advantages if successfully commercialized.
Government intervention through trade restrictions, subsidies, or regulatory requirements may artificially protect domestic manufacturers in specific markets. However, such measures typically delay rather than prevent market-based competitive outcomes, especially when performance and cost advantages are substantial.
Quality and safety concerns about Chinese products persist in some consumer segments, though independent testing consistently validates Chinese battery performance and safety claims. These perceptions may change as Chinese technology gains broader market acceptance through demonstrated reliability.
Intellectual property considerations involve complex questions about technology transfer, patent rights, and innovation ownership that may influence future competitive dynamics. However, Chinese companies increasingly develop proprietary technologies rather than relying on licensed Western innovations.
Supply chain diversification efforts by Western governments and companies aim to reduce dependence on Chinese materials and components. Success in these initiatives could theoretically alter competitive balance, though alternative supply chains typically involve higher costs and reduced efficiency.
The analysis assumes continued political and economic stability enabling market-based competition. Significant geopolitical tensions or trade disruptions could potentially alter market dynamics through non-economic mechanisms, though technological and cost advantages typically prevail over time.
Environmental and sustainability considerations may influence future market development, particularly regarding mining practices, manufacturing energy sources, and end-of-life recycling. Chinese companies increasingly emphasize sustainability initiatives to address these concerns while maintaining competitive advantages.
Conclusion
The battery industry transformation represents one of the most significant shifts in global industrial competitiveness within a single decade. Chinese manufacturers have achieved comprehensive advantages in technology, manufacturing, costs, and market position that reshape the entire electric vehicle ecosystem.
For consumers, the implications are largely positive through access to superior battery technology at competitive prices, improved vehicle performance, and faster innovation cycles. Chinese technological leadership enables better products reaching markets faster than traditional development timelines.
Investment implications favor early recognition of Chinese battery technology superiority before this becomes conventional wisdom among mainstream financial analysts. Market timing suggests optimal opportunities for positioning in leading Chinese companies while valuations still reflect incomplete recognition of competitive advantages.
The strategic implications extend beyond automotive applications to include energy storage, portable electronics, and grid infrastructure applications. Chinese battery leadership provides foundation advantages across multiple growing technology sectors that compound over time.
Western manufacturers face difficult choices between accepting technological dependency or investing heavily in technologies that may struggle to achieve commercial competitiveness. Government support can provide temporary protection but typically cannot overcome sustained technological and economic disadvantages.
The battery wars demonstrate how quickly global industrial leadership can shift when companies achieve breakthrough manufacturing capabilities combined with cost advantages and government support. This pattern may repeat across other high-technology industries as global competitive dynamics continue evolving.
For policymakers, the Chinese battery example illustrates the importance of sustained industrial policy, research investment, and manufacturing excellence in maintaining technological competitiveness. Short-term political considerations often conflict with long-term industrial strategy requirements.
The future belongs to companies that can deliver superior performance at competitive costs while scaling manufacturing to meet global demand. Current evidence strongly suggests Chinese manufacturers have achieved sustainable advantages across these critical dimensions, positioning them for continued market leadership.
Essential Resources for Industry Analysis
Understanding rapidly evolving battery technology markets requires access to professional research and analysis tools:
Research and Analytics:
- Research comprehensive market data and trends – Track industry developments and competitive positioning
- Professional content creation for technical analysis (20% OFF) – Transform complex data into accessible insights
Communication and Documentation:
- Advanced voice synthesis for professional presentations – Create compelling industry analysis content
- Newsletter platform for market insights – Share investment analysis and market developments with stakeholders
Secure Research Access:
- Secure VPN for international market research – Access global databases and research publications safely
These tools enable investors, analysts, and industry professionals to conduct comprehensive market research while maintaining security and producing professional-quality analysis for decision-making purposes.

Pingback: CATL Sodium Battery Revolution: $1,415 to $65 per kWh